Xport-A functions as a chaperone by stabilizing the first 5 transmembrane domains of Rhodopsin-1

Xport-A functions as a chaperone by stabilizing the first five transmembrane domains of rhodopsin-1 - ScienceDirect

Xport-A functions as a chaperone by stabilizing the first five transmembrane domains of rhodopsin-1 - ScienceDirect
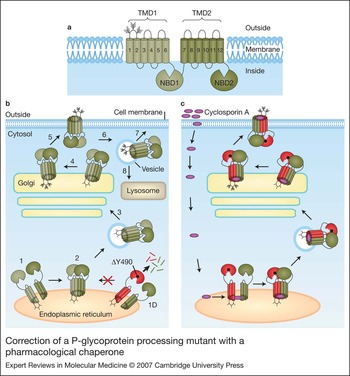
Chemical and pharmacological chaperones as new therapeutic agents, Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine

EMC is required for biogenesis of Xport‐A, an essential chaperone of Rhodopsin‐1 and the TRP channel

Full article: The role of motor proteins in photoreceptor protein transport and visual function

Rhodopsin biosynthesis defects in santa maria¹. (A) Previously proposed
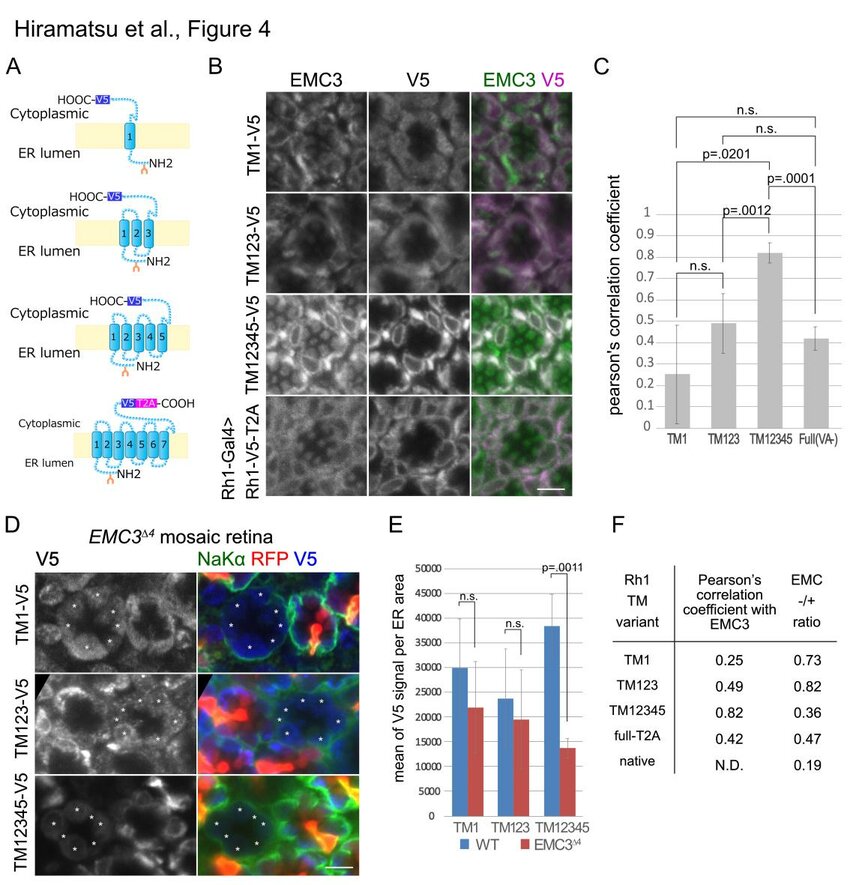
Endoplasmic reticulum membrane complex (EMC) may assist the exit of

Identification of Small Molecular Chaperones Binding P23H Mutant Opsin through an In Silico Structure-Based Approach

Xport-A functions as a chaperone by stabilizing the first five transmembrane domains of rhodopsin-1 - ScienceDirect

EMC is required for biogenesis of Xport‐A, an essential chaperone of Rhodopsin‐1 and the TRP channel

Tiago Lopes Gomes on LinkedIn: Xport-A functions as a chaperone by stabilizing the first five…
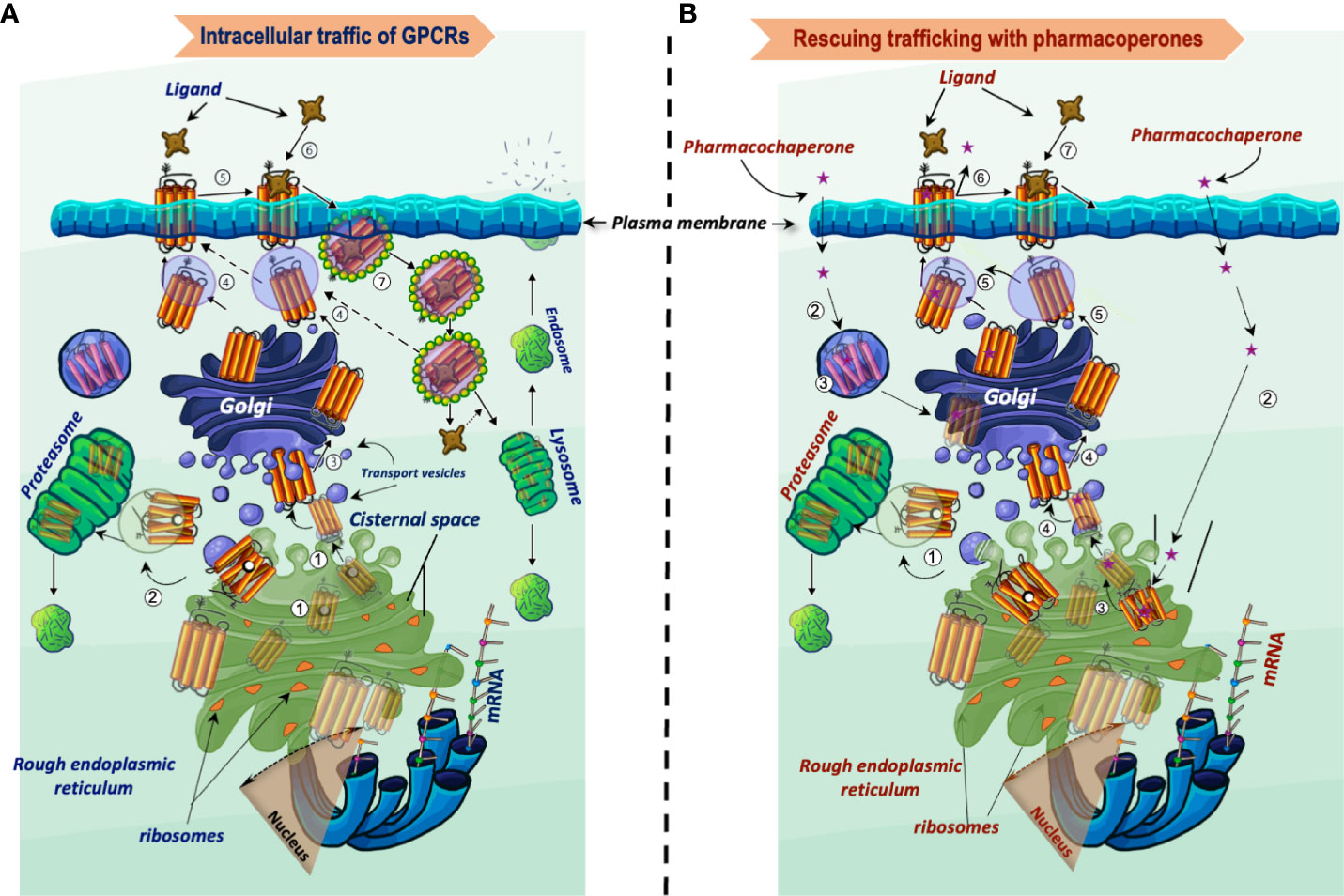
Frontiers Targeting trafficking as a therapeutic avenue for misfolded GPCRs leading to endocrine diseases

EMC is required for biogenesis and membrane insertion of Xport-A, an essential chaperone of rhodopsin-1 and the TRP channel

Rhodopsin as a Molecular Target to Mitigate Retinitis Pigmentosa